快速入门
在本教程中,我们将构建一个简单的 MCP 天气服务器并将其连接到宿主程序 Claude for Desktop。我们将从基础设置开始,然后逐步过渡到更复杂的用例。
我们要构建什么
许多 LLM(包括 Claude)目前还没有获取天气预报和严重天气警报的能力。让我们用 MCP 来解决这个问题!
我们将构建一个提供两个工具的服务器:get-alerts 和 get-forecast。然后我们将服务器连接到一个 MCP 宿主程序(在本例中是 Claude for Desktop):
为什么选择 Claude for Desktop 而不是 Claude.ai?
MCP 核心概念
MCP 服务器可以提供三种主要类型的功能:
- 资源(Resources):可以被客户端读取的类文件数据(如 API 响应或文件内容)
- 工具(Tools):可以被 LLM 调用的函数(需要用户批准)
- 提示(Prompts):帮助用户完成特定任务的预写模板
本教程主要关注工具,但如果你想了解更多关于资源和提示的内容,我们也有进阶教程。
配置环境
首先,让我们安装 uv 并设置 Python 项目和环境:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | shpowershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"安装完成后请重启终端,以确保 uv 命令可以被正确识别。
现在,让我们创建并设置项目:
# 为项目创建新目录
uv init weather
cd weather
# 创建虚拟环境并激活
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# 安装依赖
uv add mcp httpx
# 删除模板文件
rm hello.py
# 创建我们的文件
mkdir -p src/weather
touch src/weather/__init__.py
touch src/weather/server.py# 为项目创建新目录
uv init weather
cd weather
# 创建虚拟环境并激活
uv venv
.venv\Scripts\activate
# 安装依赖
uv add mcp httpx
# 清理模板代码
rm hello.py
# 创建我们的文件
md src
md src\weather
new-item src\weather\__init__.py
new-item src\weather\server.py将以下代码添加到 pyproject.toml:
...rest of config
[build-system]
requires = [ "hatchling",]
build-backend = "hatchling.build"
[project.scripts]
weather = "weather:main"将以下代码添加到 __init__.py:
from . import server
import asyncio
def main():
"""包的主入口点。"""
asyncio.run(server.main())
# 可选:在包级别暴露其他重要项
__all__ = ['main', 'server']现在让我们开始构建服务器。
构建服务器
导入包
将以下内容添加到 server.py 的顶部:
from typing import Any
import asyncio
import httpx
from mcp.server.models import InitializationOptions
import mcp.types as types
from mcp.server import NotificationOptions, Server
import mcp.server.stdio设置实例
然后初始化服务器实例和 NWS API 的基础 URL:
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
server = Server("weather")实现工具列表
我们需要告诉客户端有哪些工具可用。list_tools() 装饰器会注册这个处理程序:
@server.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]:
"""
列出可用的工具。
每个工具使用 JSON Schema 验证来指定其参数。
"""
return [
types.Tool(
name="get-alerts",
description="获取指定州的天气预警",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"state": {
"type": "string",
"description": "两字母州代码(例如 CA、NY)",
},
},
"required": ["state"],
},
),
types.Tool(
name="get-forecast",
description="获取指定位置的天气预报",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"latitude": {
"type": "number",
"description": "位置的纬度",
},
"longitude": {
"type": "number",
"description": "位置的经度",
},
},
"required": ["latitude", "longitude"],
},
),
]这里定义了我们的两个工具:get-alerts 和 get-forecast。
辅助函数
接下来,让我们添加用于查询和格式化国家气象服务 API 数据的辅助函数:
async def make_nws_request(client: httpx.AsyncClient, url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""向 NWS API 发送请求并进行适当的错误处理。"""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""将预警特征格式化为简洁的字符串。"""
props = feature["properties"]
return (
f"事件:{props.get('event', '未知')}\n"
f"区域:{props.get('areaDesc', '未知')}\n"
f"严重程度:{props.get('severity', '未知')}\n"
f"状态:{props.get('status', '未知')}\n"
f"标题:{props.get('headline', '无标题')}\n"
"---"
)实现工具执行
工具执行处理程序负责实际执行每个工具的逻辑。让我们添加它:
@server.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(
name: str, arguments: dict | None
) -> list[types.TextContent | types.ImageContent | types.EmbeddedResource]:
"""
处理工具执行请求。
工具可以获取天气数据并通知客户端变化。
"""
if not arguments:
raise ValueError("缺少参数")
if name == "get-alerts":
state = arguments.get("state")
if not state:
raise ValueError("缺少州参数")
# 将州代码转换为大写以确保格式一致
state = state.upper()
if len(state) != 2:
raise ValueError("州代码必须是两位字母(例如 CA, NY)")
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
alerts_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts?area={state}"
alerts_data = await make_nws_request(client, alerts_url)
if not alerts_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="获取预警数据失败")]
features = alerts_data.get("features", [])
if not features:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text=f"{state} 没有活跃的预警")]
# 将每个预警格式化为简洁的字符串
formatted_alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in features[:20]] # 仅取前20个预警
alerts_text = f"{state} 的活跃预警:\n\n" + "\n".join(formatted_alerts)
return [
types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=alerts_text
)
]
elif name == "get-forecast":
try:
latitude = float(arguments.get("latitude"))
longitude = float(arguments.get("longitude"))
except (TypeError, ValueError):
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="无效的坐标。请提供有效的纬度和经度数字。"
)]
# 基本坐标验证
if not (-90 <= latitude <= 90) or not (-180 <= longitude <= 180):
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="无效的坐标。纬度必须在 -90 到 90 之间,经度在 -180 到 180 之间。"
)]
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
# 首先获取网格点
lat_str = f"{latitude}"
lon_str = f"{longitude}"
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{lat_str},{lon_str}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(client, points_url)
if not points_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text=f"获取坐标 {latitude}, {longitude} 的网格点数据失败。此位置可能不受 NWS API 支持(仅支持美国位置)。")]
# 从响应中提取预报 URL
properties = points_data.get("properties", {})
forecast_url = properties.get("forecast")
if not forecast_url:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="从网格点数据获取预报 URL 失败")]
# 获取预报
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(client, forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="获取预报数据失败")]
# 格式化预报周期
periods = forecast_data.get("properties", {}).get("periods", [])
if not periods:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="没有可用的预报周期")]
# 将每个周期格式化为简洁的字符串
formatted_forecast = []
for period in periods:
forecast_text = (
f"{period.get('name', '未知')}:\n"
f"温度: {period.get('temperature', '未知')}°{period.get('temperatureUnit', 'F')}\n"
f"风: {period.get('windSpeed', '未知')} {period.get('windDirection', '')}\n"
f"{period.get('shortForecast', '无可用预报')}\n"
"---"
)
formatted_forecast.append(forecast_text)
forecast_text = f"{latitude}, {longitude} 的预报:\n\n" + "\n".join(formatted_forecast)
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=forecast_text
)]
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")运行服务器
最后,实现主函数来运行服务器:
async def main():
# 使用标准输入/输出流运行服务器
async with mcp.server.stdio.stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(
read_stream,
write_stream,
InitializationOptions(
server_name="weather",
server_version="0.1.0",
capabilities=server.get_capabilities(
notification_options=NotificationOptions(),
experimental_capabilities={},
),
),
)
# 如果你想连接到自定义客户端,这是必需的
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())你的服务器已经完成!运行 uv run src/weather/server.py 以确认一切正常。
让我们现在测试你的服务器,从现有的 MCP 宿主程序,Claude for Desktop。
测试你的服务器与 Claude for Desktop
首先,确保你已经安装了 Claude for Desktop。你可以在这里安装最新版本。
接下来,在文本编辑器中打开你的 Claude for Desktop App 配置,位于 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json。
例如,如果你已经安装了 VS Code:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json添加此配置(替换父文件夹路径):
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather",
"run",
"weather"
]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"C:\\ABSOLUTE\PATH\TO\PARENT\FOLDER\weather",
"run",
"weather"
]
}
}
}这告诉 Claude for Desktop:
- 有一个名为 “weather” 的 MCP 服务器
- 通过运行
uv --directory /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather run weather来启动它
保存文件,并重新启动 Claude for Desktop。
测试命令
首先,确保 Claude for Desktop 已经识别到我们在 weather 服务器中暴露的两个工具。你可以通过查找锤子图标 <img src="/images/claude-desktop-mcp-hammer-icon.svg" style={{display: ‘inline’, margin: 0, height: ‘1.3em’}} /> 来确认:
点击锤子图标后,你应该能看到两个工具:

如果你的服务器没有被 Claude for Desktop 识别,请查看故障排除部分获取调试建议。
现在你可以通过在 Claude for Desktop 中运行以下命令来测试你的服务器:
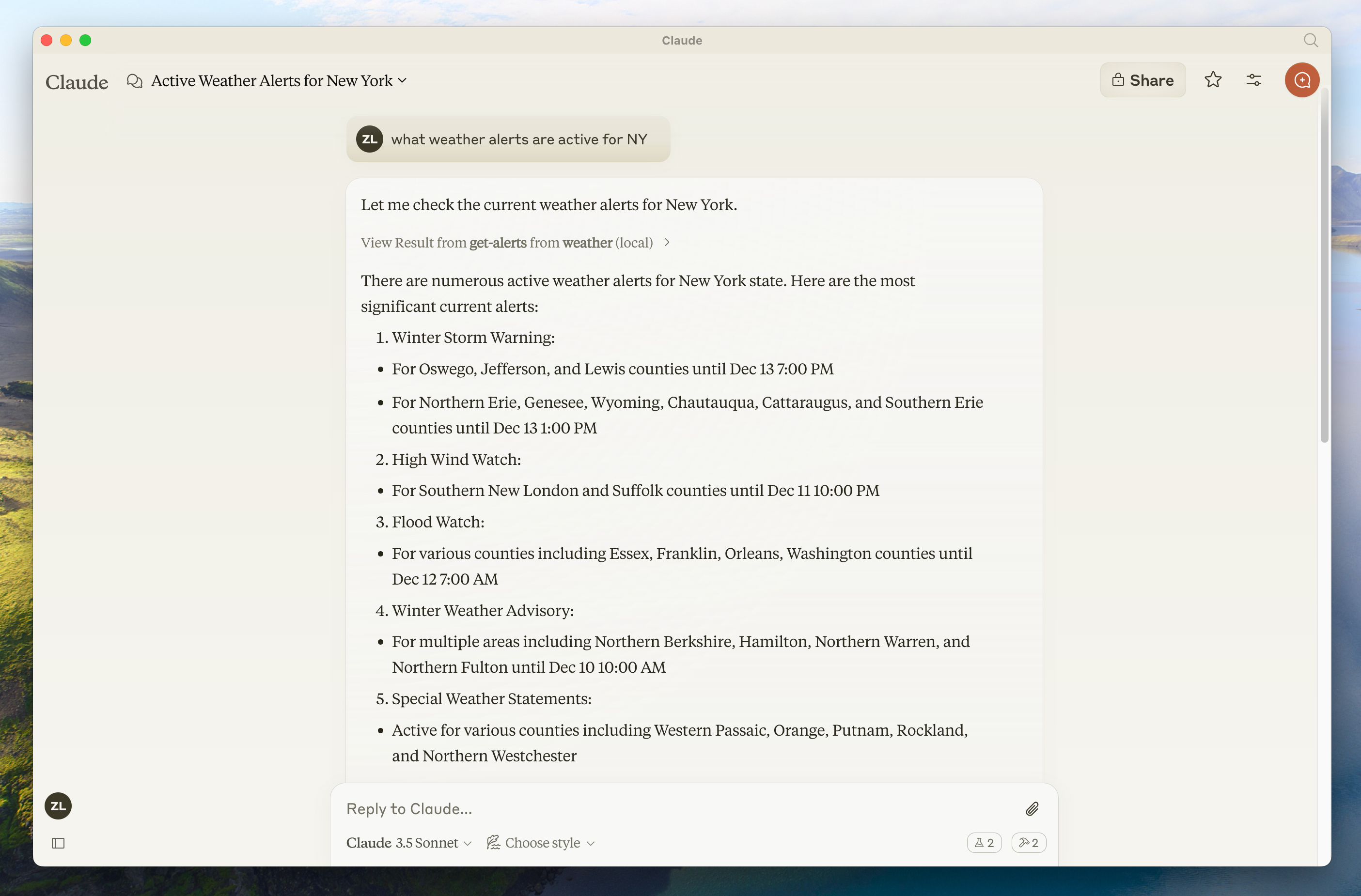
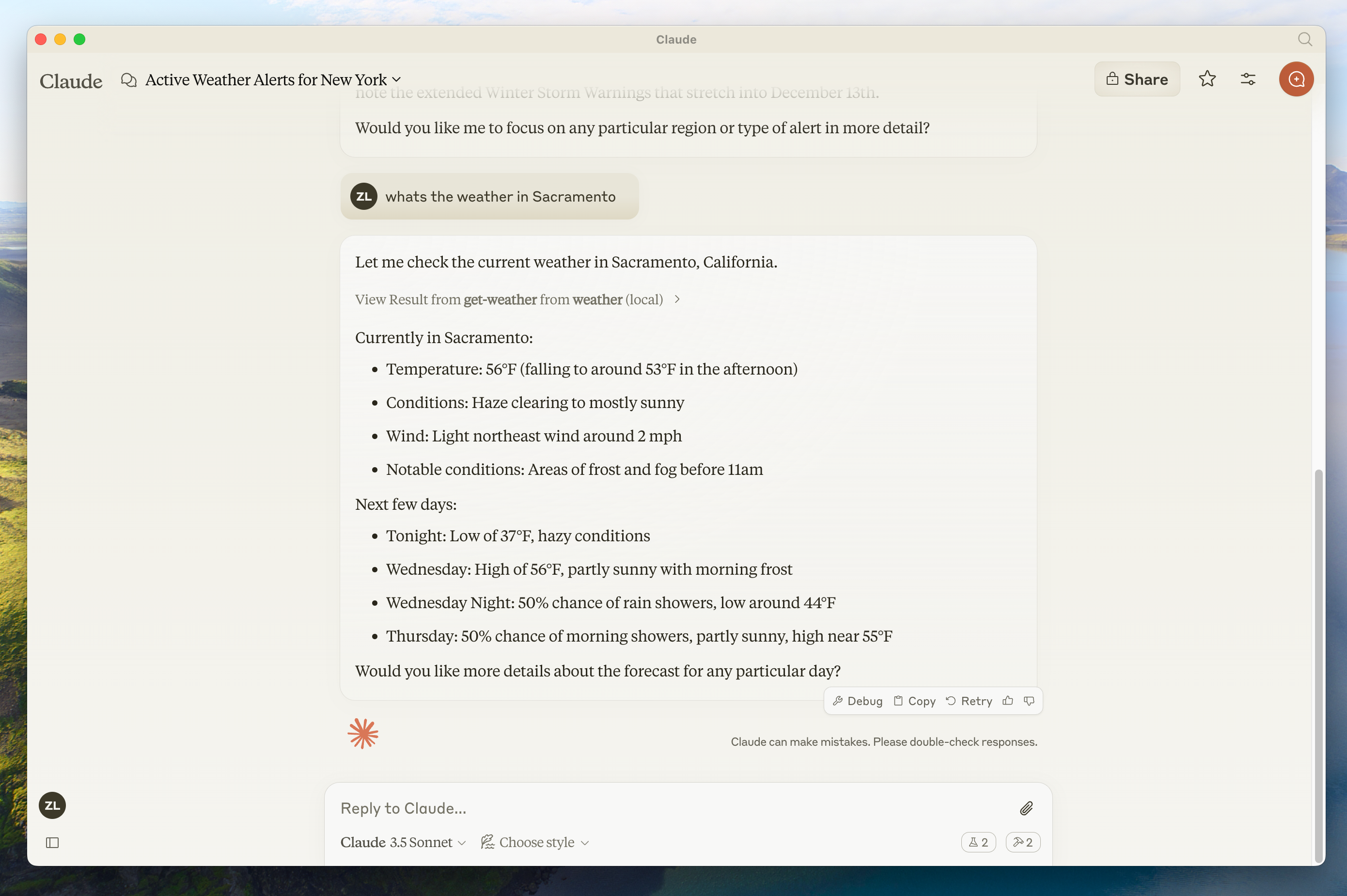
- Sacramento 的天气怎么样?
- Texas 有什么活跃的天气预警?


幕后原理
当你提出一个问题时:
- 客户端将你的问题发送给 Claude
- Claude 分析可用的工具并决定使用哪个工具
- 客户端通过 MCP 服务器执行选定的工具
- 结果返回给 Claude
- Claude 组织一个自然语言响应
- 响应显示给你!
故障排除
天气 API 问题
错误:获取网格点数据失败
这通常意味着:
- 坐标在美国境外
- NWS API 出现问题
- 你被限制请求频率
解决方案:
- 确认你使用的是美国境内的坐标
- 在请求之间添加小延迟
- 检查 NWS API 状态页面
错误:[州] 没有活跃的预警
这不是错误 - 只是意味着该州当前没有天气预警。可以尝试查询其他州或在恶劣天气期间再次检查。
Claude for Desktop 集成问题
服务器没有在 Claude 中显示
- 检查你的配置文件语法
- 确保项目路径正确
- 完全重启 Claude for Desktop
你也可以这样检查 Claude 的日志:
# 检查 Claude 的错误日志
tail -n 20 -f ~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp*.log工具调用静默失败
如果 Claude 尝试使用工具但失败:
- 检查 Claude 的日志是否有错误
- 验证你的服务器是否正常运行
- 尝试重启 Claude for Desktop